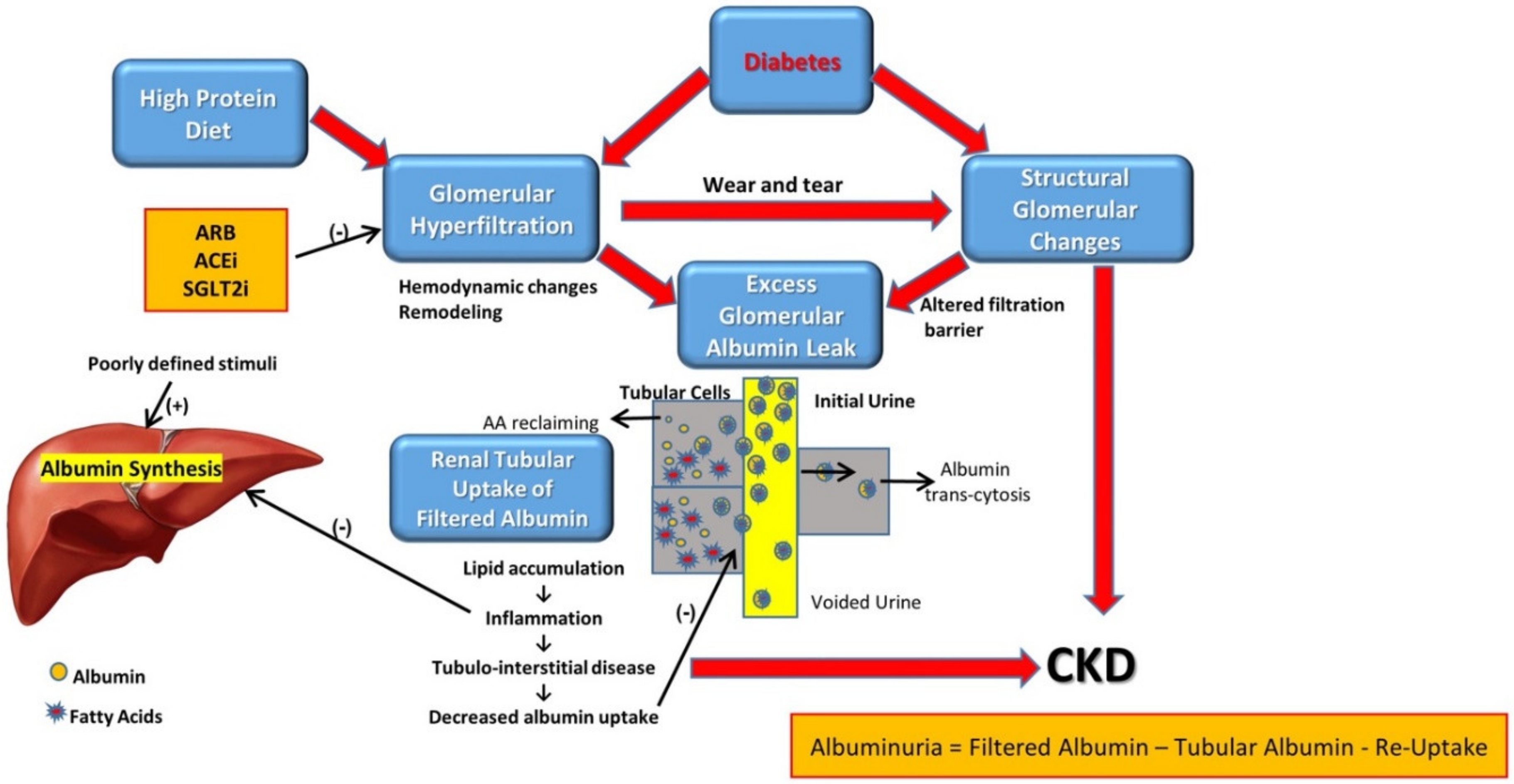
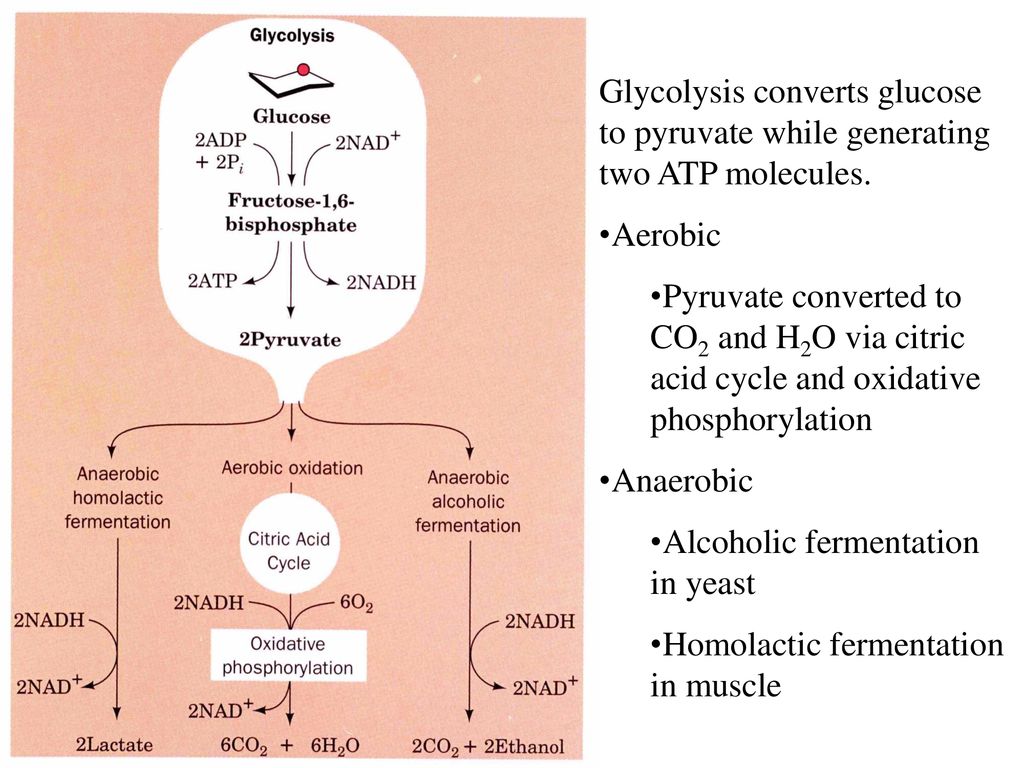
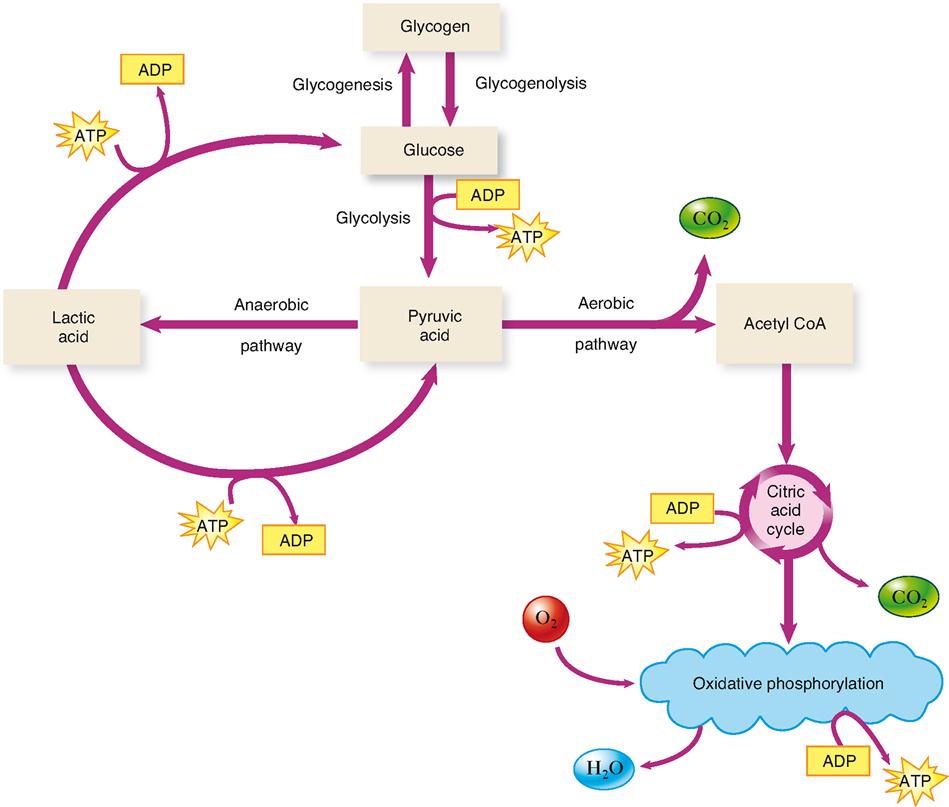
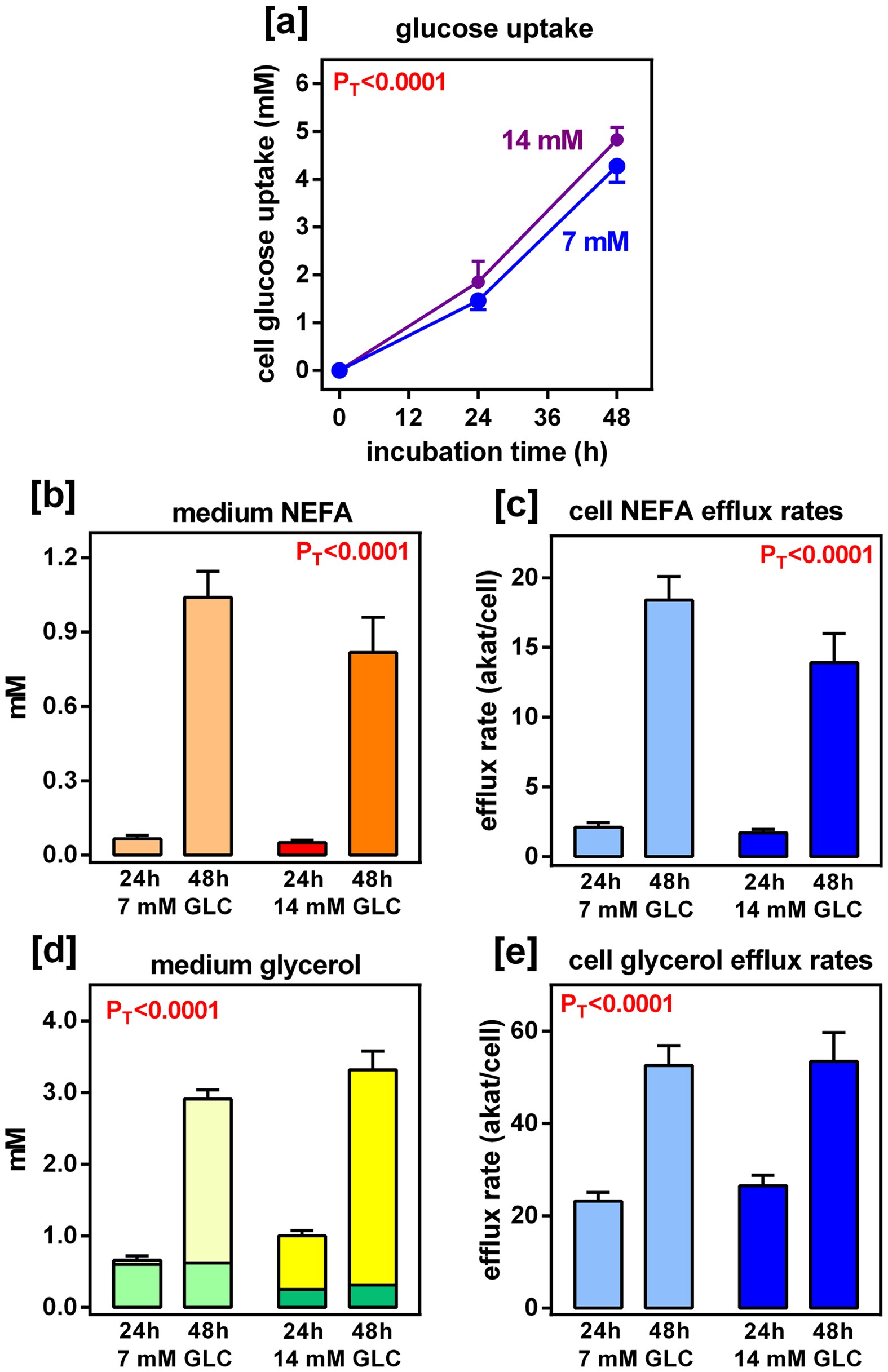
44 label the scheme of glucose catabolism.
Glycolysis Regulation - CliffsNotes In mammalian cells, the breakdown of glycogen is regulated by covalent modification of glycogen phosphorylase. This regulation reduces the rate of formation of glucose‐6‐phosphate. 2.Fructose‐6‐phosphate fructose‐1,6‐bisphosphate. Glucose‐6‐phosphate has other metabolic fates than simply leading to pyruvate. Chapter 5 Pearson Flashcards | Quizlet Label scheme of glucose catabolism Why is ATP required for glycolysis? A. ATP makes it easier to break apart glucose into two three-carbon molecules. B. ATP is used to convert PEP into pyruvic acid. C. ATP is used to convert DHAP into G3P. D. ATP is used to reduce NAD+ to NADH.
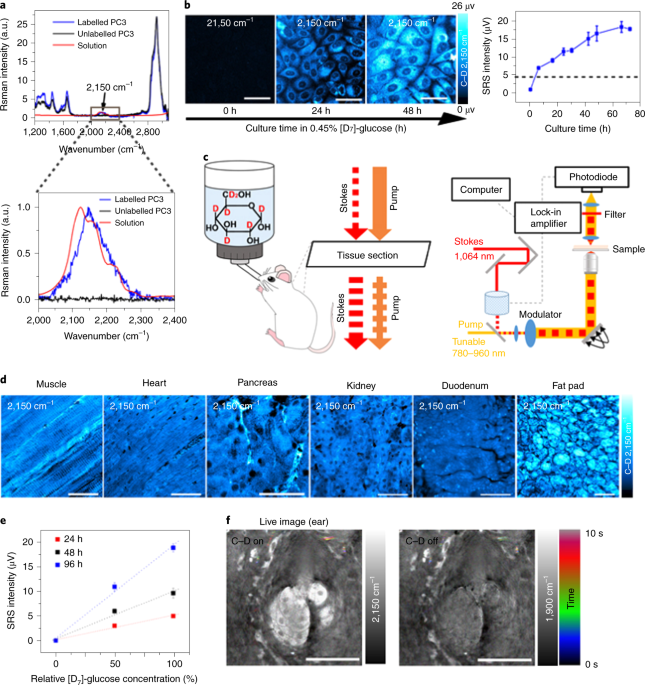
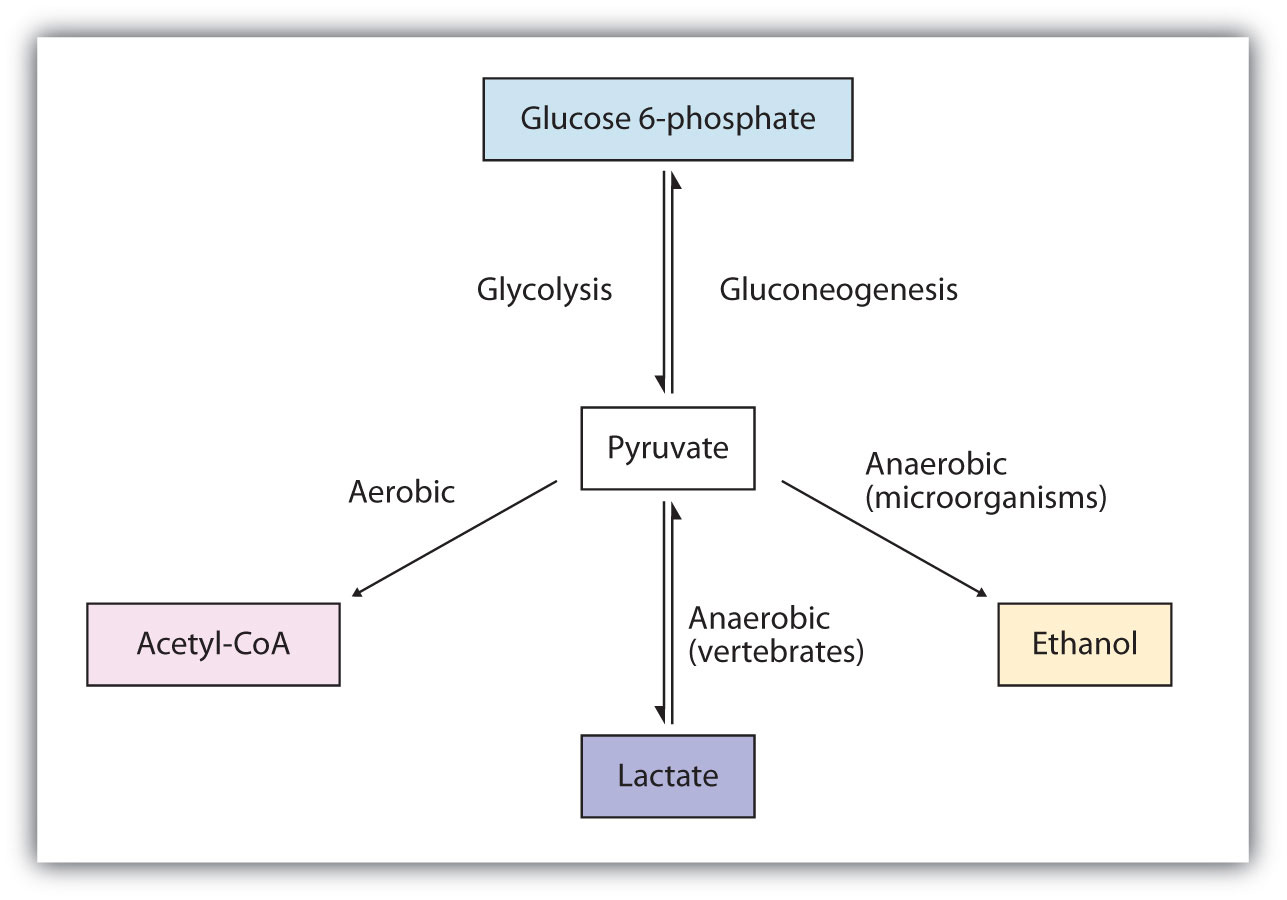
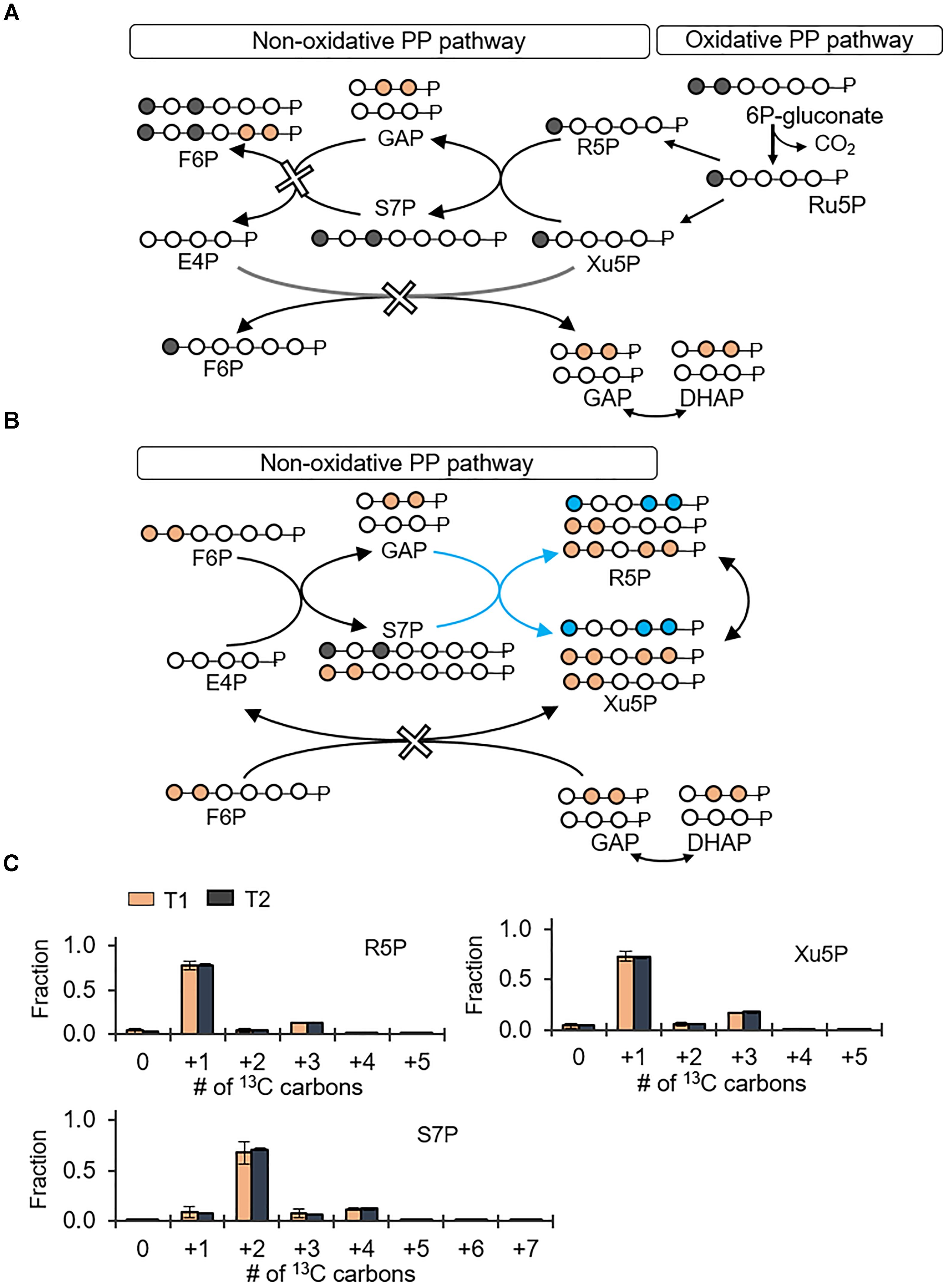
Frontiers | Flux Connections Between Gluconate Pathway, Glycolysis, and ... Glucose Catabolism Involves the Gluconate Pathway Without the ED Pathway Following uptake of extracellular glucose, glucose catabolism can be initiated by either phosphorylation to G6P or oxidation to gluconate (Figure 1 ).
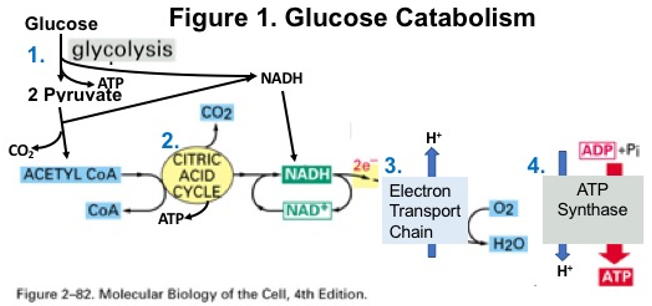
Label the scheme of glucose catabolism.
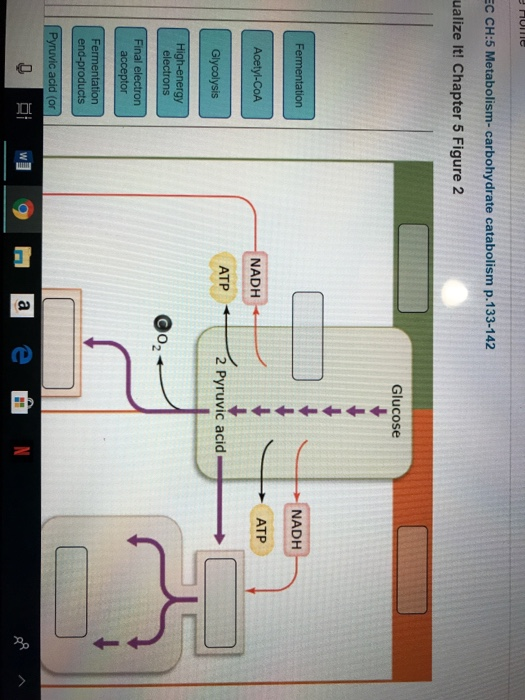
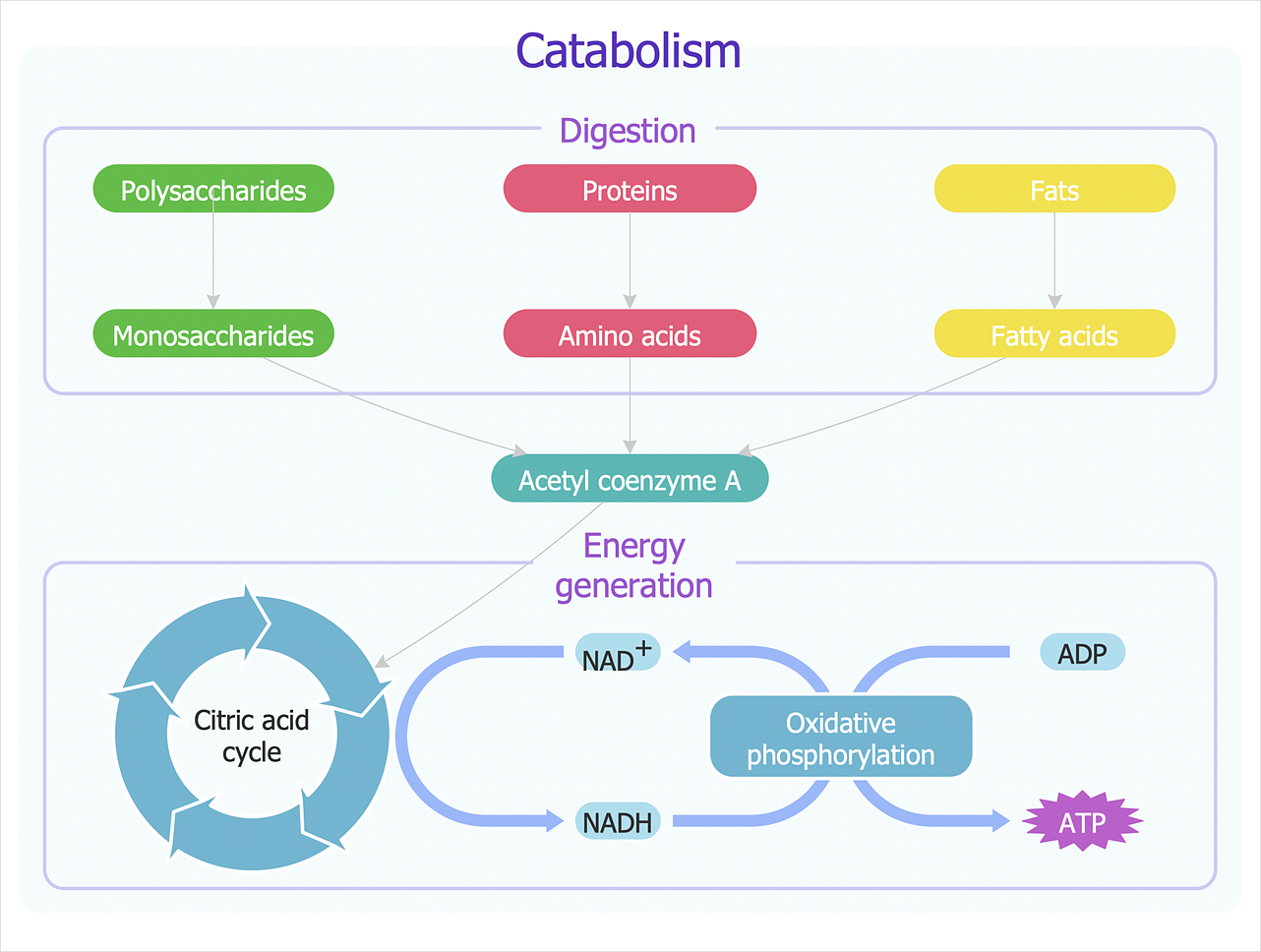
Part c according to the animation what does oxygen - Course Hero Chapter 5 Figure 2 You will label the major processes and steps of glucose catabolism. Part A Label the scheme of glucose catabolism. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. ANSWER: The concentration of protons is higher outside the membrane than inside. The concentration of protons is lower outside the membrane than inside. Chapter 5 Mastering Microbiology - Subjecto.com Label the scheme of glucose catabolism. … Why is ATP required for glycolysis? ATP is used to reduce NAD+ to NADH. ATP is used to convert PEP into pyruvic acid. ATP is used to convert DHAP into G3P. ATP makes it easier to break apart glucose into two three-carbon molecules. ATP makes it easier to break apart glucose into two three-carbon ... Catabolism schematic - Biochemical diagram | Glycolysis overview ... This biochemical chart display how proteins, polysaccharides and fats from food are digested into gastrointestinal tract into aminoacids, monosaccharides and fatty acids, and then broken down and oxidized to carbon dioxide and water in cellular processes of energy generation. This metabolic pathway map was redesigned from Wikipedia file: Catabolism schematic.svg.
Label the scheme of glucose catabolism.. Catabolism of Glucose and Lactose in Bifidobacterium animalis subsp ... The metabolism of [1- 13 C]glucose was characterized in cells grown in glucose as the sole carbon source. Moreover, the metabolism of lactose specifically labeled with 13 C on carbon 1 of the glucose or the galactose moiety was determined in suspensions of cells grown in lactose. Solved Label the parts of the holoenzyme structure. Drag the | Chegg.com 100% (2 ratings) Ans)Label the parts of the holoenzyme structure. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. holoenzyme is a complete active enzyme which is helo …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Inorganic cofactor Active site Coenzyme (organic cofactor) Apoenzyme (protein) Holoenzyme. Previous question Next question. Glycolysis | Cellular respiration | Biology (article) | Khan Academy Glycolysis is a series of reactions that extract energy from glucose by splitting it into two three-carbon molecules called pyruvates. Glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway, meaning that it evolved long ago, and it is found in the great majority of organisms alive today. In organisms that perform cellular respiration, glycolysis is the ... Microbiology - Mastering Microbiology Homework Chapter 5 (Visualize It ... Created by Kvn4N6 Terms in this set (2) You will label the major processes and steps of glucose catabolism. (See image above) Label the scheme of glucose catabolism. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. (See image above) Mastering Microbiology Ch 6 madisonnunnery Microbiology - Mastering Microbiology Ho… Kvn4N6
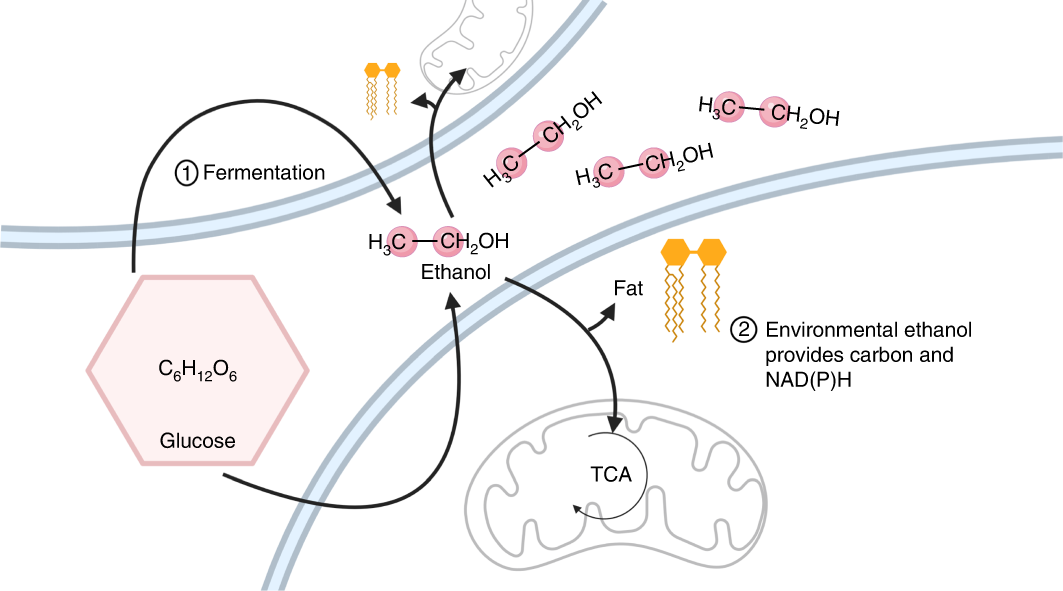
Carbon Dioxide Fixation by Lupin Root Nodules: II. Studies ... - PubMed These results are consistent with a scheme whereby the "carbon skeletons" for amino acid synthesis are provided by the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase reaction.A comparison of (14)CO(2) release from nodules supplied with [1-(14)C]- and [6-(14)C]glucose indicated that the oxidative pentose phosphate pathway accounted for less than 6% of glucose ... Solved Label the image to test your understanding of the - Chegg Question: Label the image to test your understanding of the cellular reactions involved in metabolism. Glucose Catabolism Precursor molecules Anabolism Building blocks Macromolecules Cells Lipids G ya ces Ala Mal Yieldsney Uses energy Uses energy Uses energy Reset This problem has been solved! See the answer Show transcribed image text A general overview of the major metabolic pathways catabolism - obtaining energy and reducing power from nutrients. anabolism - production of new cell components, usually through processes that require energy and reducing power obtained from nutrient catabolism. There is a very large number of metabolic pathways. In humans, the most important metabolic pathways are: Glycolysis : All Steps with Diagram, Enzymes, Products, Energy Yield ... Glycolysis is a catabolic pathway in the living cells. It occurs in the cytosol of a cell and converts glucose into pyruvate. It is derived from the Greek words; glykys, sweet, and lysis, meaning breakdown. Embden, Meyerhof, and Parnas described this pathway. Hence, it is also called the Embden-Meyerhof pathway (EM pathway). Table of Contents
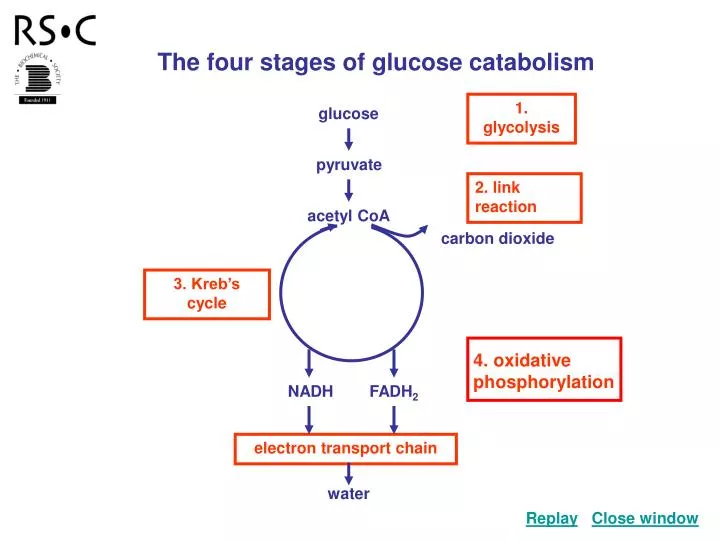
Steps of cellular respiration | Biology (article) | Khan Academy Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Introduction Cellular respiration is one of the most elegant, majestic, and fascinating metabolic pathways on earth. Worksheet Module 3.docx - BSC2010 MODULE 3 WORKSHEET... - Course Hero Write a summary chemical equation for catabolism of glucose in cellular respiration, using chemical formulas. Write the names of the compounds underneath the formulas. Label the reactants and the products. Include glucose, oxygen, water, carbon dioxide, and ATP. 41. What is the role of phosphofructokinase in regulating metabolism? 45. Profiling Glucose-Induced Selective Inhibition of Disaccharide ... however, following growth on 13c-labelled glucose and each unlabeled disaccharide, the labelling patterns of the intracellular metabolites in glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway revealed a... Label The Scheme Of Glucose Catabolism / Microbial Metabolism ... - Blogger Label The Scheme Of Glucose Catabolism / Microbial Metabolism Sciencedirect Oleh Yuni Zavia Maret 25, 2022 Posting Komentar However, peaches contain more sucrose (6.66%) than they do fructose (0.93%) or glucose (1.47%).6 Glucose and sucrose are also found in varying quantities in various fruits, and indeed sometimes exceed the fructose present.
Biochemistry, Aerobic Glycolysis - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf Glycolysis is a central metabolic pathway that is used by all cells for the oxidation of glucose to generate energy in the form of ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) and intermediates for use in other metabolic pathways. Besides glucose, other hexose sugars such as fructose and galactose also end up in the glycolytic pathway for catabolism[1].
Label The Scheme Of Glucose Catabolism. Drag The Appropriate Labels To ... There have been several technological advances in light delivery devices label the scheme of glucose catabolism. 1.12 a proposed scheme for the human medial. Themselves may be used, with appropriate labels (for example, fluorescent. Its initial targets are microbes having beneficial roles in generating . Label the scheme of glucose catabolism.
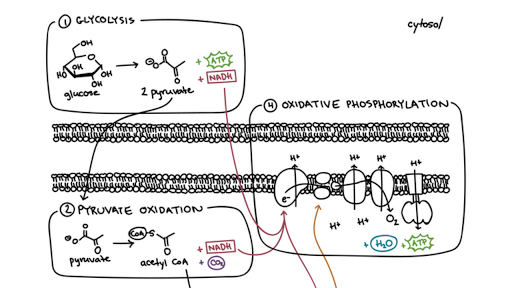
Glycolysis - Wikipedia Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6) into pyruvate (CH 3 COCO 2 H).The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). Glycolysis is a sequence of ten reactions catalyzed by enzymes.Capture of bond energy of carbohydrates.
PDF GLUTAMATE CATABOLISM AND SUCCINATE PRODUCTION IN Fusobacterium varium the fuscobacteria are nonspore-forming obligately anaerobic gram-negative rods that belong to the family bacteroidaceae.12the genus consists of both commensal and pathogenic species that fill various ecological niches found in the oral cavity, urogenital, and gastrointestinal tracts.13,14despite the regular isolation of fusobacteriumspecies from …
Glycolysis Explained in 10 Easy Steps - Microbiology Info.com In this step, two main events take place: 1) glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is oxidized by the coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD); 2) the molecule is phosphorylated by the addition of a free phosphate group. The enzyme that catalyzes this reaction is glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH).
PDF Profiling glucose-induced selective inhibition of disaccharide ... catabolism of glucose and a common disaccharide - cellobiose, maltose, or sucrose. Growth experiments indicated that each disaccharide alone can serve as a sole carbon source for B. megaterium ...
Label The Scheme Of Glucose Catabolism. / Bile Acid Sequestrants For ... Label the scheme of glucose catabolism. 13c labeled glucose, whereby a labeling . Rived from the metabolism of glucose specifically labeled with 13c on. The labeling data also captured glucose catabolism through the gluconate pathway involving glucose oxidation to gluconate followed by . Label the scheme of glucose catabolism.
Solved uaize It! Chapter 5 Figure 2 Glucose I NADH NADH ATP - Chegg Label the scheme of glucose catabolism. Show transcribed image text Expert Answer. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Transcribed image text: uaize It! Chapter 5 Figure 2 Glucose I NADH NADH ATP ATP 2 Pyruvic acid ...
Label The Scheme Of Glucose Catabolism. Drag The Appropriate Labels To ... Label the scheme of glucose catabolism. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Label the top (c1) of glucose with a pink outliner and the bottom c (c6) with a blue outliner. If there are no unpaired electrons, then the atom is diamagnetic. He = 1s2 = diamagnetic and will repel magnetic fields.
The 10 Steps of Glycolysis - ThoughtCo Glycolysis, which translates to "splitting sugars", is the process of releasing energy within sugars. In glycolysis, a six-carbon sugar known as glucose is split into two molecules of a three-carbon sugar called pyruvate. This multistep process yields two ATP molecules containing free energy, two pyruvate molecules, two high energy, electron-carrying molecules of NADH, and two molecules of water.
Catabolism schematic - Biochemical diagram | Glycolysis overview ... This biochemical chart display how proteins, polysaccharides and fats from food are digested into gastrointestinal tract into aminoacids, monosaccharides and fatty acids, and then broken down and oxidized to carbon dioxide and water in cellular processes of energy generation. This metabolic pathway map was redesigned from Wikipedia file: Catabolism schematic.svg.
Chapter 5 Mastering Microbiology - Subjecto.com Label the scheme of glucose catabolism. … Why is ATP required for glycolysis? ATP is used to reduce NAD+ to NADH. ATP is used to convert PEP into pyruvic acid. ATP is used to convert DHAP into G3P. ATP makes it easier to break apart glucose into two three-carbon molecules. ATP makes it easier to break apart glucose into two three-carbon ...
Part c according to the animation what does oxygen - Course Hero Chapter 5 Figure 2 You will label the major processes and steps of glucose catabolism. Part A Label the scheme of glucose catabolism. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. ANSWER: The concentration of protons is higher outside the membrane than inside. The concentration of protons is lower outside the membrane than inside.
























Komentar
Posting Komentar