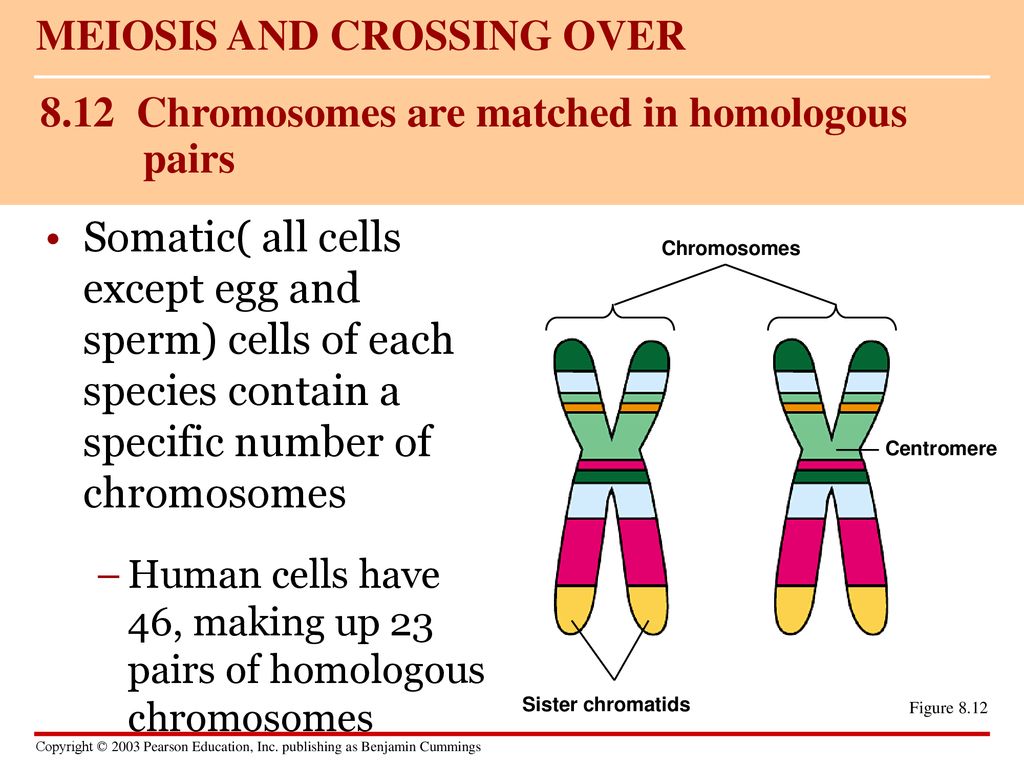
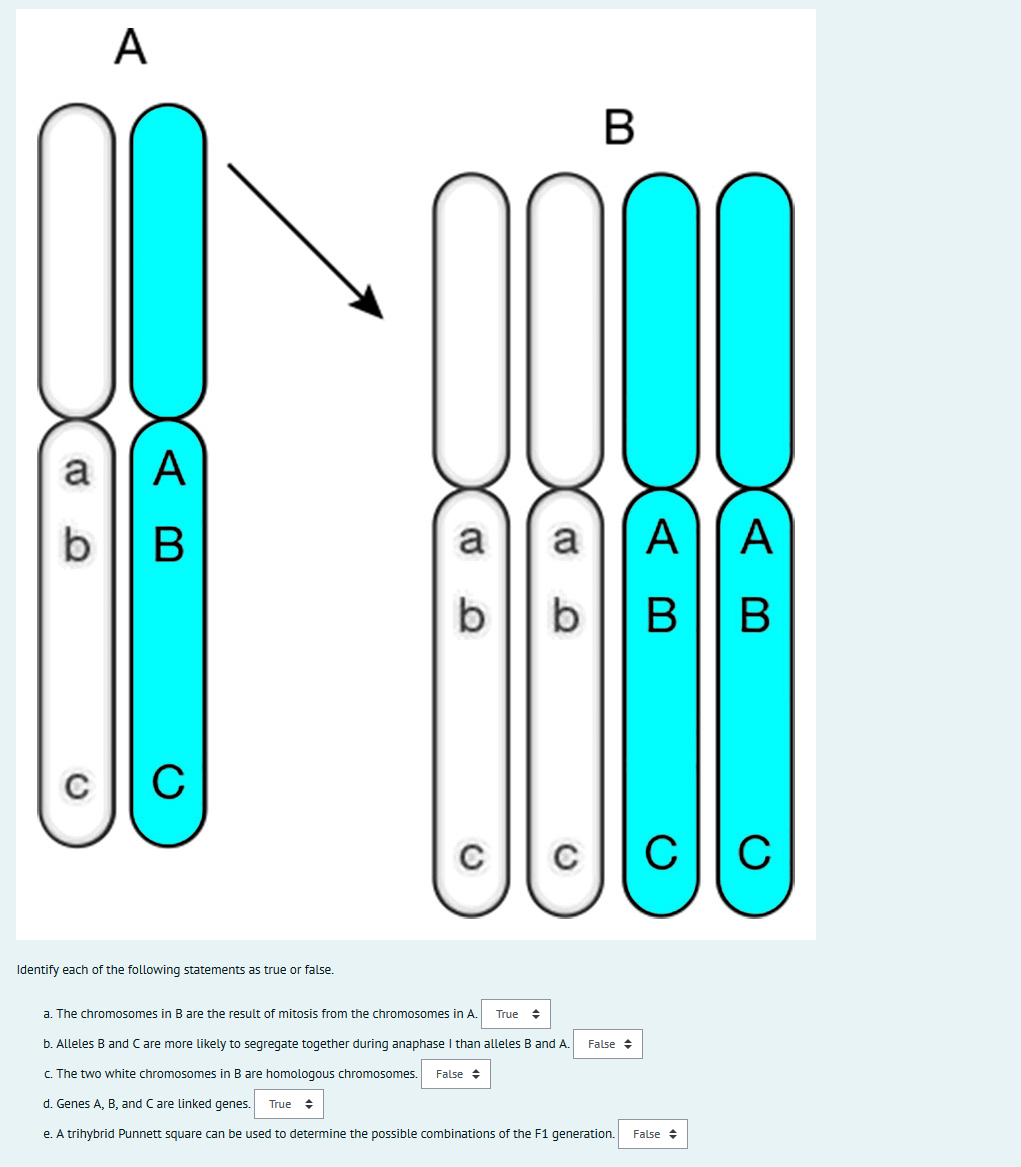
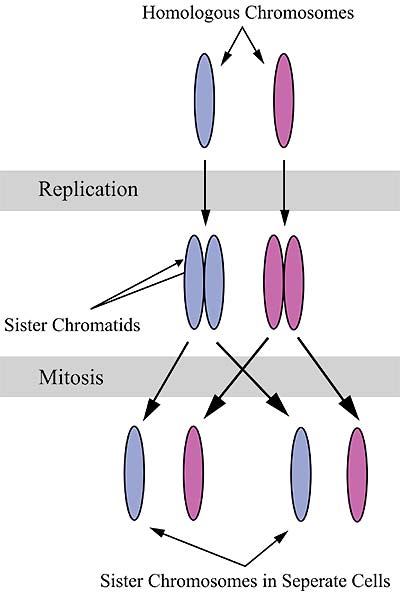
42 homolougous chromosomes
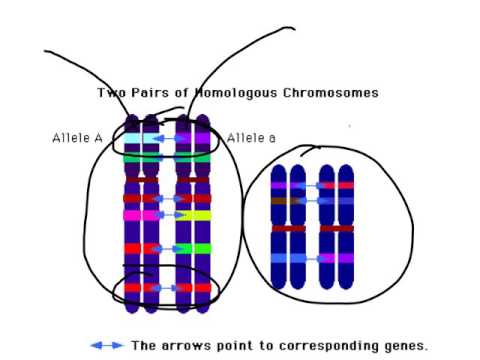
Chromosomes (article) | Cell cycle | Khan Academy The two chromosomes in a homologous pair are very similar to one another and have the same size and shape. Most importantly, they carry the same type of genetic information: that is, they have the same genes in the same locations. However, they don't necessarily have the same versions of genes. Chromosome pairs (article) | Chromosomes | Khan Academy Key points: Every species has its own specific number of chromosomes. For example, humans have 46 chromosomes in a typical body cell. Many species have chromosomes that come in matched pairs. For example, the 46 chromosomes in a human cell can be organized into 23 pairs. These paired chromosomes are called homologous chromosomes.
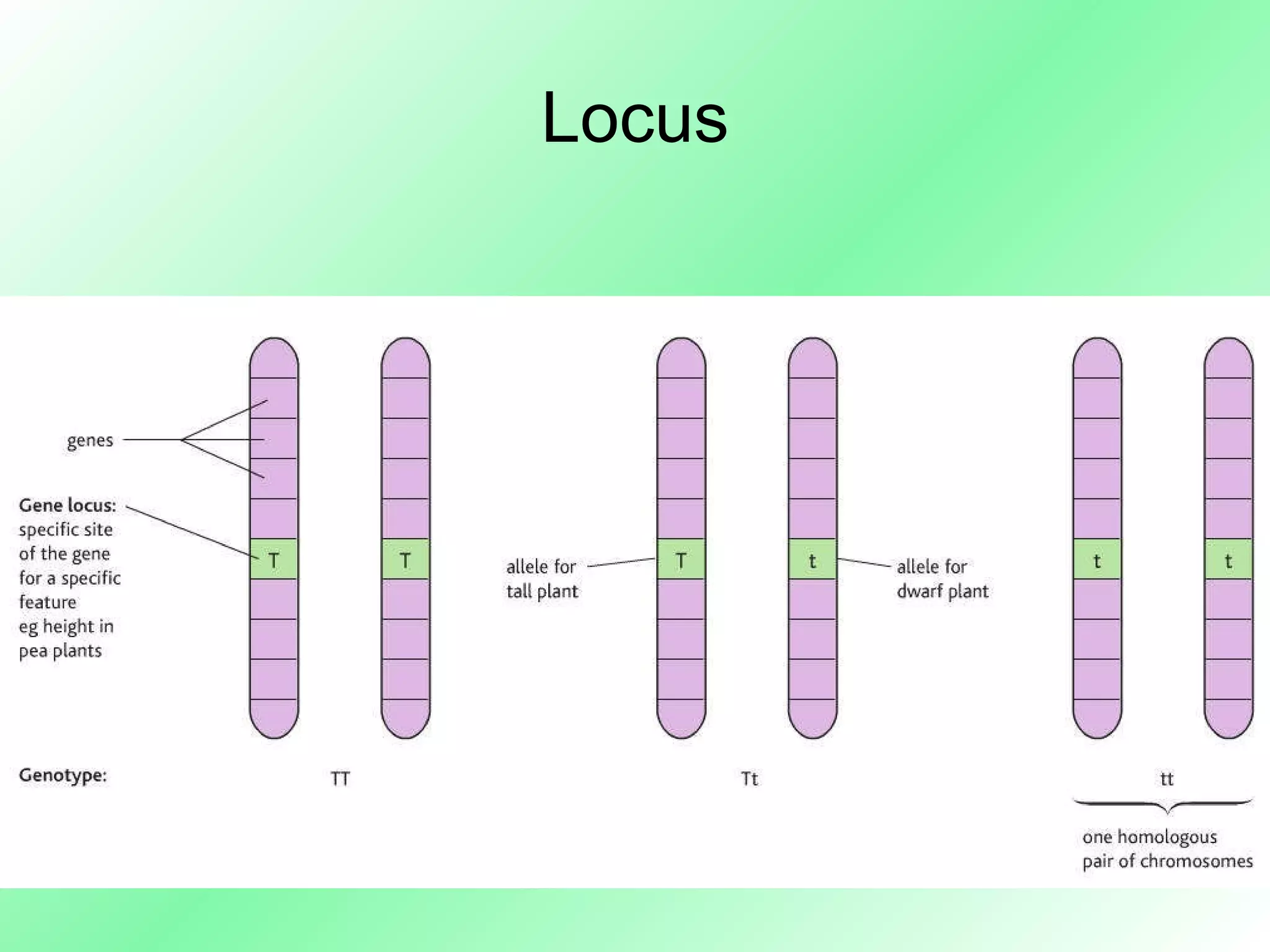
Homologous Chromosome - Structure and Function - BYJUS What are Homologous Chromosomes? Homologous Chromosomes are made of chromosomal pairs of the same length and centromere positions for the genes corresponding to the same loci. Typically one of the chromosomes is inherited from the father and the other from the mother.
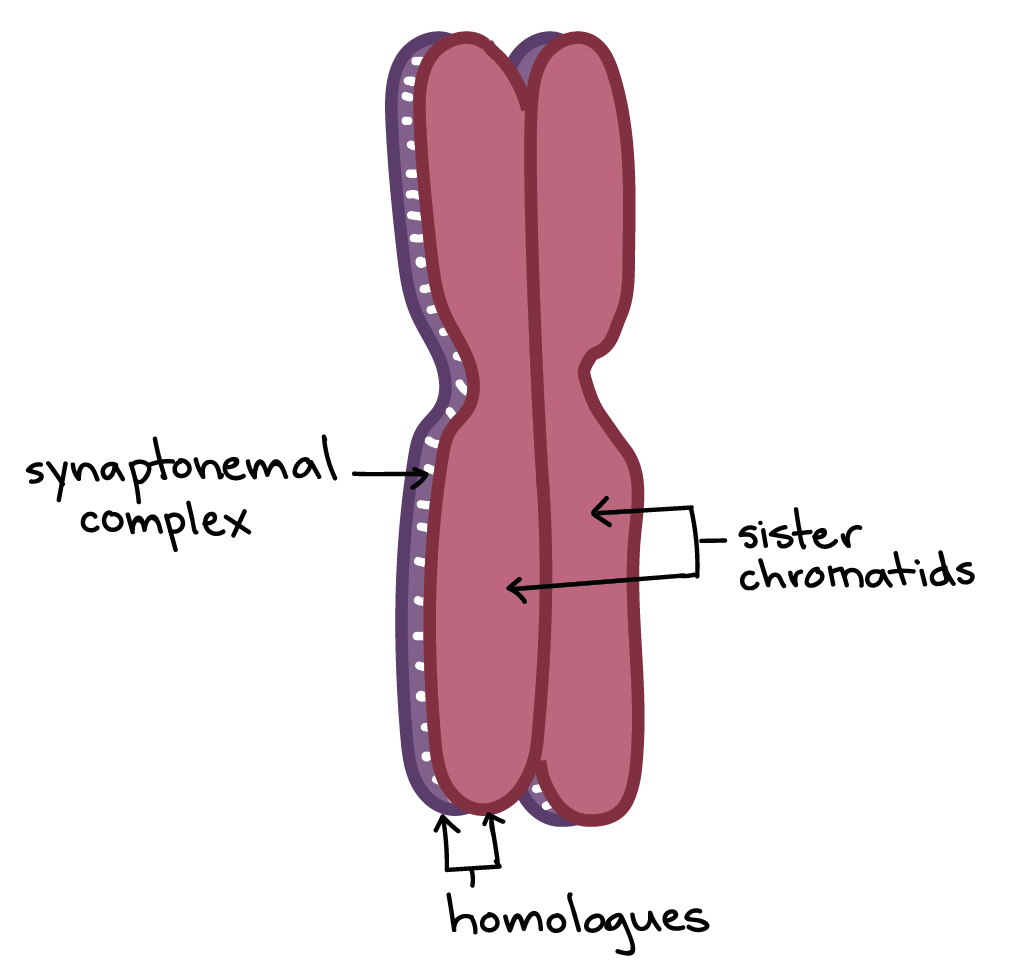
Homolougous chromosomes
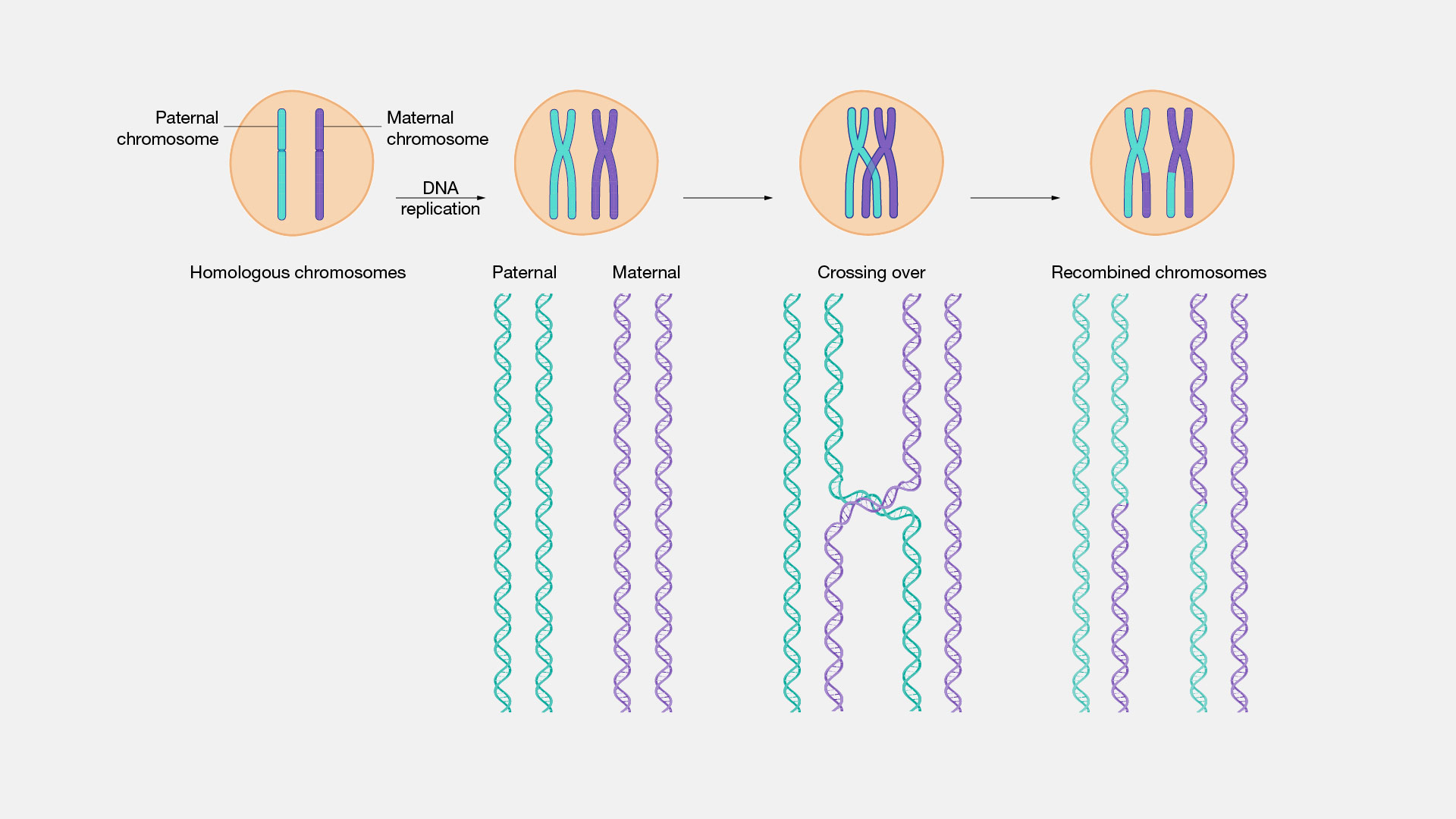
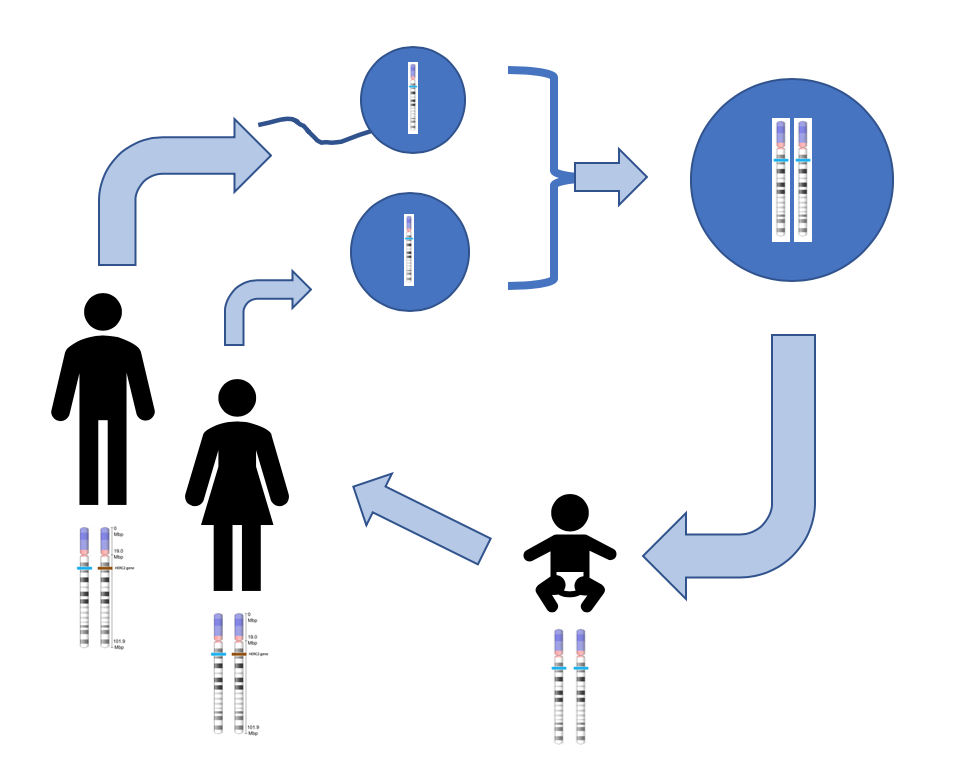
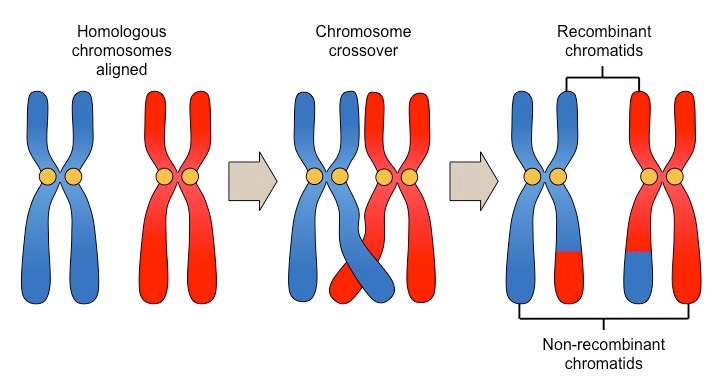
Homologous chromosome - Definition and Examples - Biology Online Dictionary A homologous chromosome pertains to one of a pair of chromosomes with the same gene sequence, loci, chromosomal length, and centromere location. A homologous pair consists of one paternal and one maternal chromosome. In humans, there are a total of 46 chromosomes in the nucleus of a somatic cell. Crossing Over - Genome.gov Definition. Crossing over, as related to genetics and genomics, refers to the exchange of DNA between paired homologous chromosomes (one from each parent) that occurs during the development of egg and sperm cells (meiosis). This process results in new combinations of alleles in the gametes (egg or sperm) formed, which ensures genomic variation ... Homologous Definition & Meaning - Merriam-Webster homologous chromosomes b chemistry : belonging to or consisting of a chemical series (see series sense 6) whose successive members have a regular difference in composition especially of one methylene group 2 biology : derived from or developed in response to organisms of the same species a homologous tissue graft Did you know?
Homolougous chromosomes. What Is A Homologous Chromosome? | Biology Explorer What Is A Homologous Chromosome? Each living cell, be it animal, plant, or bacterial cells, has its genetic material (DNA) packaged into coiled structures called chromosomes. While they are known to be located in the nucleus, chromosomes are only visible when the cell is undergoing division. Homologous chromosome | definition of homologous chromosome by Medical ... homologous chromosome: One of a pair of chromosomes that contain genes for the same traits; one is maternal in origin, the other paternal. See also: chromosome Homologous Chromosomes: Definition & Examples - Biology Dictionary Homologous chromosomes are two pieces of DNA within a diploid organism which carry the same genes, one from each parental source. In simpler terms, both of your parents provide a complete genome. Each parent provides the same 23 chromosomes, which encode the same genes. So, our cells carry 46 total chromosomes, in two copies. Homologous Chromosomes: Definition, Function and Challenges - Science ABC Homologous chromosomes are the pairs of chromosomes of a similar length, centromere position and gene composition. The alleles on these chromosomes may be different, resulting in genetic variation in offspring, and they both direct phenotypic effects in the organism.
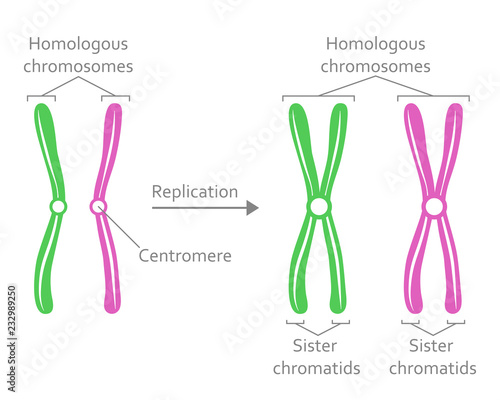
Homologous Chromosome - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Homologous chromosome recombination occurs in meiosis and plays an important role in genetic diversity, and is also a key determinant in the unique gene profile of an individual. This naturally occurring process has important biological implications in oogenesis, which occurs through DNA repair. The process spans the pachytene, leptotene, and ... Homologous chromosomes Definition & Meaning | Dictionary.com homologous chromosomes [ (huh- mol-uh-guhs) ] A pair of matching chromosomes in an organism, with one being inherited from each parent. The New Dictionary of Cultural Literacy, Third Edition Copyright © 2005 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved. Homologous chromosomes | definition of homologous chromosomes by ... homologous chromosomes: Etymology: Gk, homos, same, chroma color, soma body any two chromosomes in a diploid somatic cell that are identical in size, shape, and gene loci. In humans there are 22 pairs of homologous chromosomes and 1 pair of sex chromosomes, with 1 member of each pair derived from the mother and the other from the father. Homologous chromosome - Wikipedia Homologous chromosomes are made up of chromosome pairs of approximately the same length, centromere position, and staining pattern, for genes with the same corresponding loci. One homologous chromosome is inherited from the organism's mother; the other is inherited from the organism's father.
Homologous Chromosomes: Definition and Function - Science Terms Homologous Chromosomes Definition. Homologous chromosomes are a pair of DNA molecules which contain information for the same genes, though each homologous chromosome may carry different alleles.A diploid organism (like a human) carries two copies of each gene, one on each part of this pair of homologous chromosomes. Homologous chromosome - Simple English Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Homologous chromosomes are the pairs of chromosomes in a diploid organism. They are the chromosomes which pair during meiosis. [1] With the exception of the sex chromosomes, each pair has the gene loci in the same positions on each chromosome, and the centromere in the same position. A Genetics Definition of Homologous Chromosomes - ThoughtCo Homologous chromosomes separate during the first meiotic division and the resulting sister chromatids separate during the second division. At the end of meiosis, four distinct daughter cells are produced. Each of these is haploid and contains only half of the chromosomes of the original cell. Difference Between Homologous and Homeologous Chromosomes Homologous chromosomes are the chromosomes that are similar in length, the composition of the gene and the position of the centromere. However, the alleles in chromosomes may differ, which lead to variations in offspring of the same parents. In humans, there are 23 pairs of chromosomes.
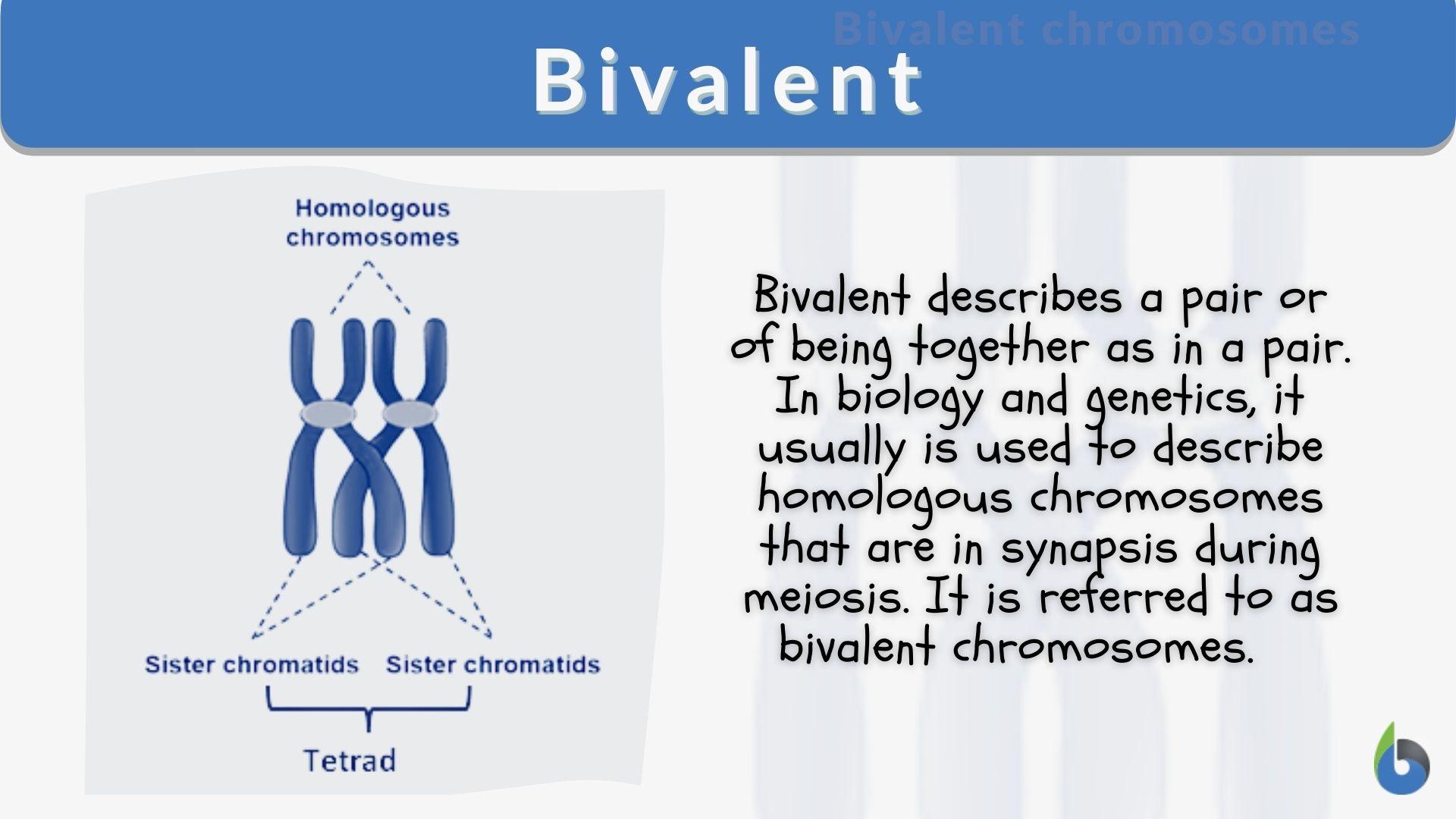
homologous chromosomes definition A pair of chromosomes made up of two homologs. Homologous chromosomes have corresponding DNA sequences and come from separate parents; one homolog comes from the mother and the other comes from the father. Homologous chromosomes line up and synapse during meiosis. 2. chromosomes in different species that have retained most of the same genes ...
Homologous Chromosome Flashcards | Quizlet Homologous Chromosomes Chromosome pairs (one from each parent) that are similar in length, gene position-banding, and centromere location. Homologous chromosomes are similar but not identical. Each carries the same genes in the same order, but the alleles for each trait may not be the same. Maternal
Homologous Definition & Meaning - Merriam-Webster homologous chromosomes b chemistry : belonging to or consisting of a chemical series (see series sense 6) whose successive members have a regular difference in composition especially of one methylene group 2 biology : derived from or developed in response to organisms of the same species a homologous tissue graft Did you know?
Crossing Over - Genome.gov Definition. Crossing over, as related to genetics and genomics, refers to the exchange of DNA between paired homologous chromosomes (one from each parent) that occurs during the development of egg and sperm cells (meiosis). This process results in new combinations of alleles in the gametes (egg or sperm) formed, which ensures genomic variation ...
Homologous chromosome - Definition and Examples - Biology Online Dictionary A homologous chromosome pertains to one of a pair of chromosomes with the same gene sequence, loci, chromosomal length, and centromere location. A homologous pair consists of one paternal and one maternal chromosome. In humans, there are a total of 46 chromosomes in the nucleus of a somatic cell.





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-764793193-e8f09cb6bc4843c0a7363db1d0a34c95.jpg)





![PDF] Initiation of homologous chromosome pairing during ...](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/80e7625725b9caeae7274cd8135342bf8adde7e1/2-Figure1-1.png)















Komentar
Posting Komentar